Google Prompting Essentials course
Estimated reading time: 26 minutes
I reviewed Google’s Prompting Essentials course on Coursera so you don’t have to. Here are some insights I gained from the course, alongside my thoughts on whether you should spend $49 on it.
Quick Overview
| Platform | Coursera |
| Name of the Course | Google Prompting Essentials |
| Provider | |
| Duration | Approx. 6 hours (1 week) |
| Enrolled | 46,033 |
| Difficulty | Beginner |
| Rating | 4.8 (533 reviews) // if can put stars png on it |
| Price | $49 Or Coursera Plus |
This course consists of 4 modules, covering everything from AI prompting for everyday tasks to using AI prompts as your personal creative and expert partner.
Table of contents
Module 1: Start Writing Prompts Like a Pro
Videos: 13 | Readings: 6 | Assignments: 4
The first module kicks off with an introduction to the course, starting with the term “prompting” and how it plays a key role in using gen AI. It explains how AI can get your work done faster, turning tasks that once took hours manually into something quick and effortless.
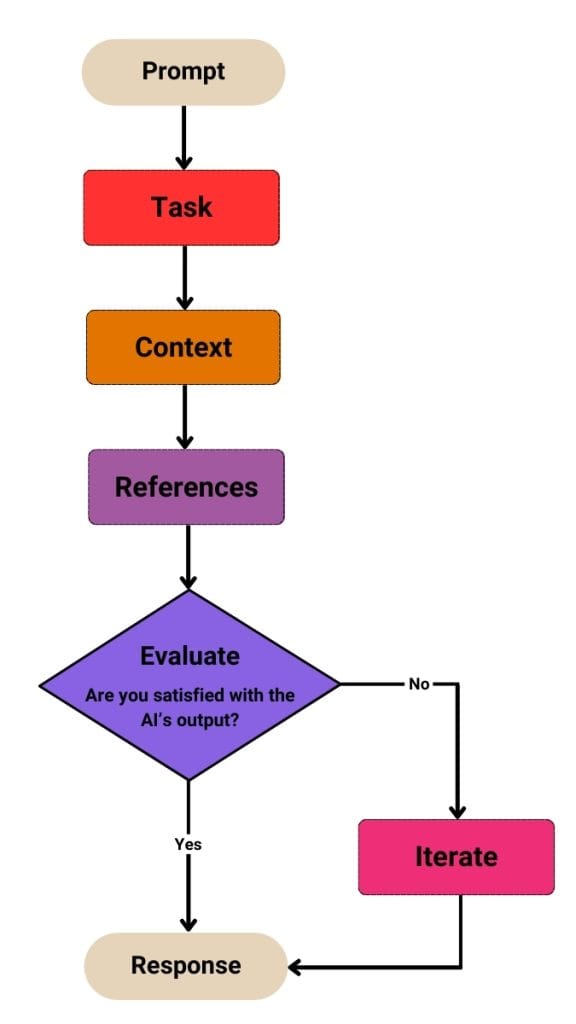
5 Step Prompt Framework
This module covers two main concepts, the first being the “5-Step Prompt Framework.” This framework acts as a formula for writing high-quality prompts and serves as the foundation of the entire course, applied throughout all upcoming modules. Here’s the 5-step framework for crafting effective prompts:
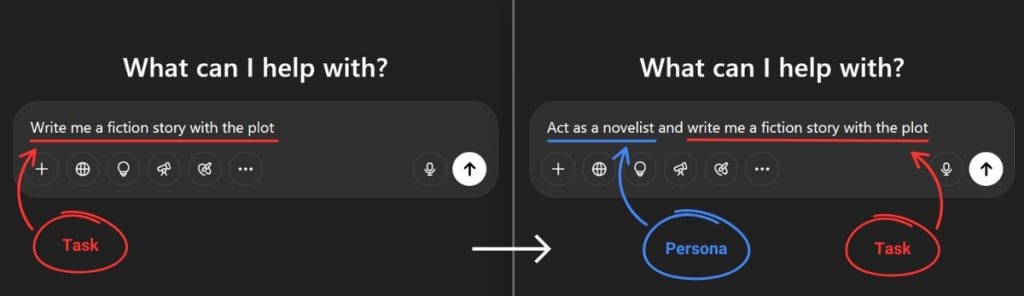
Task
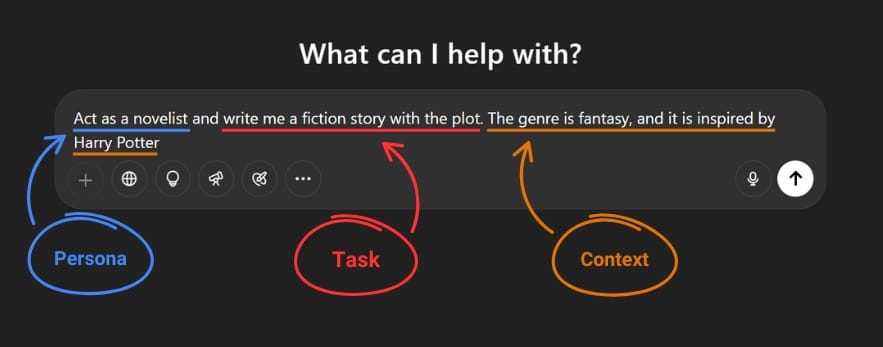
The first step in the 5 Step Prompt Framework is Task. In this case, Task refers to what you want the AI to generate. Instead of simply asking, “Write me a fiction story with the plot,” enhance the prompt by assigning the AI a role. For example, rather than making a generic request, try prompting:
“Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story with the plot.”
This technique is called Persona and helps the AI generate more specific and contextually relevant responses.
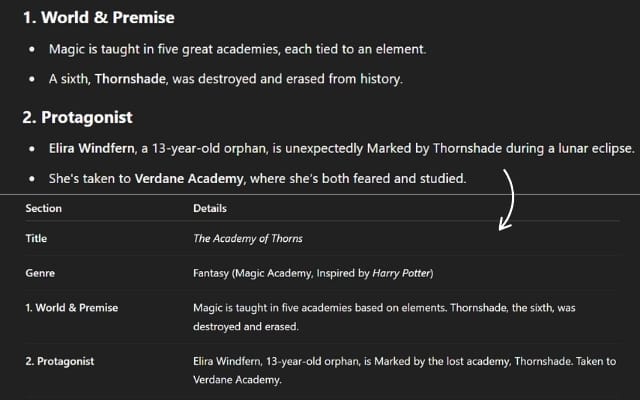
Once you establish the persona, the next step is determining the format in which the AI should present the information. By default, generative AI often outputs responses in lists and bullet points. However, to make the information more structured and easier to digest, you can prompt the AI to organize the response into a table.
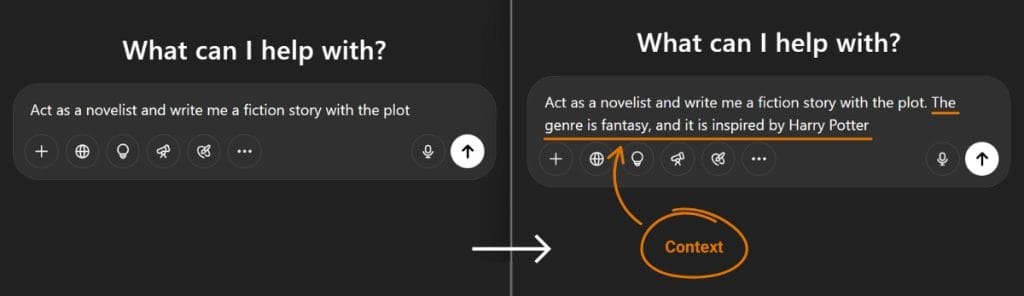
Context
The second step in the framework is Context. The general rule is that the more context you provide, the better and more accurate the AI’s response will be.
Let’s take the previous example:
“Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story with the plot.”
By adding more context, you can refine the AI’s output:
“Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story with the plot. The genre is fantasy, and it is inspired by Harry Potter.”
This technique is called Context and helps the AI generate more targeted and personalized responses.
References
The third step in the Framework is References. A reference is when you provide examples to the AI, which can be in the form of pictures, documents, or text samples.
This step is especially useful when you have a clear idea of what you want but find it difficult to describe in words. Since AI excels at analyzing examples, providing references makes it easier for the AI to understand and follow your vision.
For this example, I’ll be attaching a picture as the Reference to the previous prompt.

Evaluate
The fourth step in the Framework is Evaluate. This step is straightforward. It involves reviewing the AI’s response and checking if it aligns with the previous steps in the framework.
If the response meets all the criteria, then you’ve completed the prompt framework. If it doesn’t, you can move on to the final step in the framework.
Iterate
The final step in the Framework is Iterate. This step highlights that prompting is an ongoing process where you may need to revisit previous steps and refine your prompts until you are fully satisfied with the AI’s response.
The course even has an acronym for it: ABI – Always Be Iterating.
4 Iteration Methods
Second on the concept is the “4 Iteration Methods.” Prompting is not a one-time process. Sometimes, gen AI may not produce the desired result on the first attempt. As the course mentioned, “Always Be Iterating,” the more you evaluate and iterate your prompts, the better the AI’s response will be. Here are the 4 methods you can try to improve your prompts.
Case example of iteration in prompt engineering
Revisit the Prompting Framework
The first method involves revisiting the 5-Step Prompt Framework, focusing on Task, Context, and References. You may need to provide additional context or include more references to improve the AI’s response.
Separate Prompt into Shorter Sentences
Sometimes, AI can become overwhelmed by complex prompts. The second method solves this by breaking your prompt into smaller tasks.
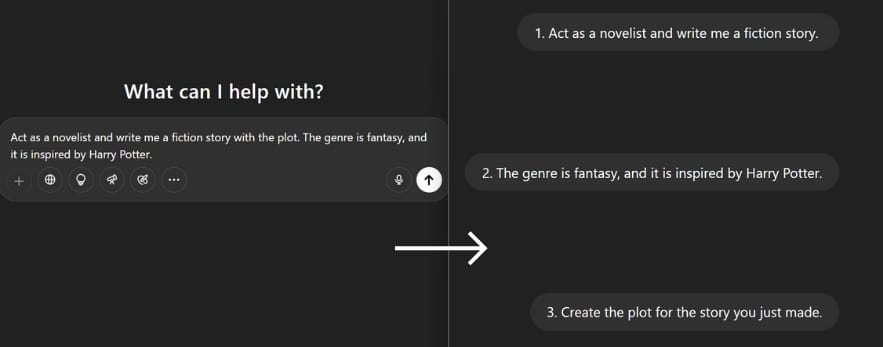
Let’s take this “long” prompt as an example:
“Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story with the plot. The genre is fantasy, and it is inspired by Harry Potter.”
You can break this prompt into shorter sentences and input them as separate prompts like this:
Input 1st prompt → receive output → follow-up with 2nd prompt → receive output → repeat, until all of the tasks have been inputted.
Here’s the example from the prompt above:
- Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story.
- The genre is fantasy, and it is inspired by Harry Potter.
- Create the plot for the story you just made.
By using this method, the AI can process one small task at a time, leading to more precise and structured results rather than handling everything at once.
Try Different Phrasing or switching to an Analogous Task
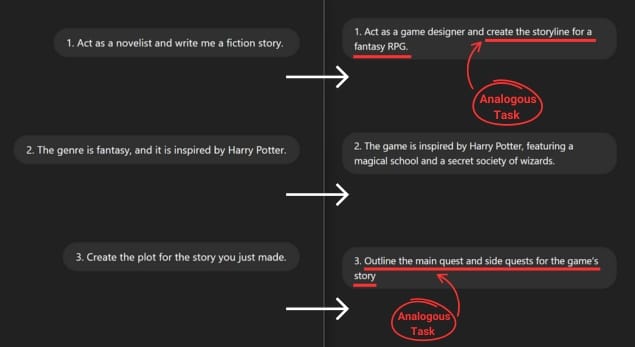
The third method involves rephrasing the prompt or switching to an analogous task. An analogous task is one that is closely related to what you want to achieve but different enough to generate a fresh response from the AI.
Let’s take the previous example, where we broke the prompt into shorter sentences, and now rephrase it using an analogous task:
- Act as a novelist and write me a fiction story. → Act as a game designer and create the storyline for a fantasy RPG.
- The genre is fantasy, and it is inspired by Harry Potter. → The game is inspired by Harry Potter, featuring a magical school and a secret society of wizards.
- Create the plot for the story you just made. → Outline the main quest and side quests for the game’s story.
By changing the prompt from “write a fiction story” to “create a storyline for an RPG game,” you’re asking the gen AI to approach the task from a new perspective, which might result in a better and more insightful response.
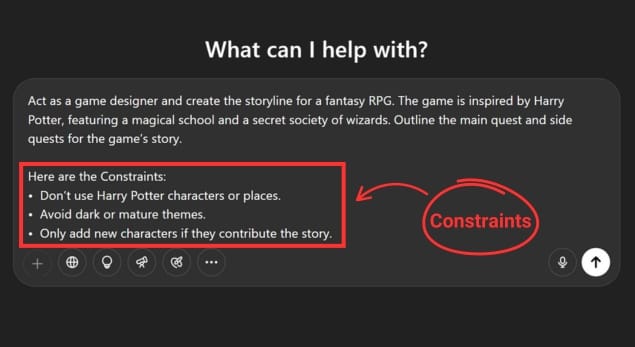
Introduce Constraints
The last method from the “4 Iteration Methods” focuses on introducing constraints in your prompt. Take the prompt above as an example and let’s add constraints to it.
- Don’t use Harry Potter characters or places.
- Avoid dark or mature themes.
- Only add new characters if they contribute the story.
Adding constraints to your prompt helps the gen AI narrow down its outputs and give you something much more personalized. Keep in mind that the more constraints you add, the more specific and personalized your output becomes.
Multimodal Prompting
There are various types of modalities you can use to interact with gen AI tools like ChatGPT or Gemini. Modalities refer to the different formats or mediums through which information is communicated. These include text, images, video, audio, and code. These AI models can process multiple modalities and mix them within both inputs and outputs.
Multimodal prompting is when you combine two or more modalities within a single prompt. For example, combining text and image to generate a response.

Case example of multimodal model
AI Hallucination & Biases
Hallucination happens when a generative AI tool produces outputs that are incorrect and doesn’t make sense. This often occurs when the input prompt is too vague or unclear. A well-known example is when ChatGPT incorrectly stated that the word “strawberry” contains two R’s.

The example above shows an AI hallucination causing a harmless mistake. However, AI hallucinations can also lead to fatal errors with harmful effects.
Fatal AI hallucination with harmful effects
Biases can also cause AI tools to generate misleading or unfair responses. Since gen AI models are trained on human-generated content, they may reflect real-world stereotypes, gender biases, or biased representations of certain groups.
To avoid biased outputs, it’s important to write detailed prompts and to Always Be Iterating.
Instead of “Workman”, try using “Worker”.
This small change helps the AI generate responses that are more inclusive, representing both male and female perspectives rather than defaulting to male only.
Another important lesson from this course is the value of using AI responsibly. It recommends applying the “human in the loop” approach, which involves always reviewing and verifying the AI’s outputs before using them. Here are considerations from the course when using AI responsibly.
//pic12 showing considerations when using AI responsibly
Apply human-in-the-loop approach when using AI
Module 2: Design Prompts for Everyday Work Tasks
Videos: 13 | Readings: 6 | Assignments: 4
Module 2 covers practical examples of how to use generative AI in everyday work tasks. It demonstrates how to apply the 5 Step Prompting Framework and the 4 Iteration Methods to write emails, brainstorm ideas, and summarize text while adjusting the tone and style of the text output.
Write emails with AI
One of the most practical applications of AI is writing emails faster and more efficiently. In this course, you’ll learn how to improve email productivity with AI using the 5 Step Prompting Framework.
For example, let’s say you need to write an email to your employees about a new gym schedule. Here’s how to structure your prompt:
Persona:
“I am a gym manager.”
Context:
“We have a new gym schedule.”
Task:
“Write an email informing our staff of the new schedule. Highlight that the Monday, Wednesday, and Friday Cardio Blast class has changed from 7:00 AM to 6:00 AM.”
Format:
“Make the email professional, friendly, and brief so readers can skim it easily.”
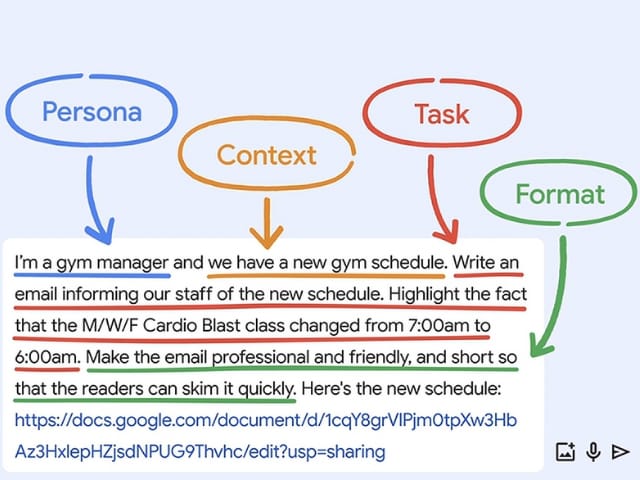
Now let’s iterate on the prompt to shift the tone for gym members:
Task:
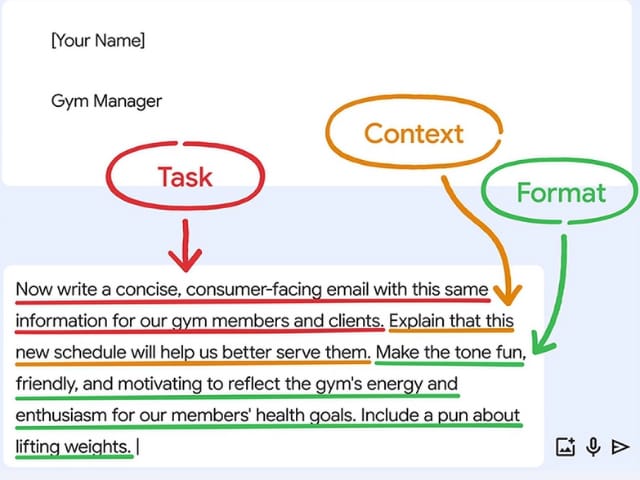
“Now write a concise, consumer-facing email with this same information for our gym members and clients.”
Context:
“Explain that this new schedule will help us better serve them.”
Format:
“Make the tone fun, friendly, and motivating to reflect the gym’s energy and enthusiasm for our members’ health goals. Include a pun about lifting weights.”
With this approach, what would normally take 10 minutes to write manually can be done in under a minute using gen AI. Since many of us write emails every day, these time saving benefits quickly add up and can save you hours in the long run.
Brainstorm ideas with AI
In this lesson, you will learn how to write effective prompts to generate creative ideas using gen AI, following the 5 Step Prompting Framework.
Imagine this scenario: you need to plan a launch for a new video game. This is where brainstorming with AI becomes incredibly useful. AI can help you generate marketing strategies, develop timelines, and create promotional ideas targeted to your audience.
Persona:
“I’m a marketer for a well-known video game producer.”
Context:
“I’m planning the launch of a new medieval fantasy role-playing game.”
Task:
“Provide a rough timeline for the year leading up to its launch. Also include some pre-launch marketing ideas to generate buzz around the game.”
//pic15 showing the complete version of the prompt (timestamp 2:10 brainstorm ideas tha buzz)
Now let’s iterate on the prompt to expand its reach:
“Now provide pre-launch ideas that will appeal to a global audience of young adults.”
By evaluating and iterating your prompt, AI can generate more targeted and personalized ideas. You can use AI to plan a product launch or generate content ideas. This way, you can be more creative and productive in your work.
Summarize with AI
Sometimes, you need to summarize long and complex documents. This is where AI text summarization becomes incredibly helpful. Generative AI can process large blocks of text, extract the most important information, and even transform the content into new resources.
To summarize a lengthy document, you’ll need to use a gen AI tool with a long context window, which enables the model to process large amounts of information at once.
Let’s say you have a report to summarize, using the prompting framework, let us extract the key points in the report:
Task:
“Summarize this report in an outline. Focus only on the most essential points.”
Format:
“In an outline”
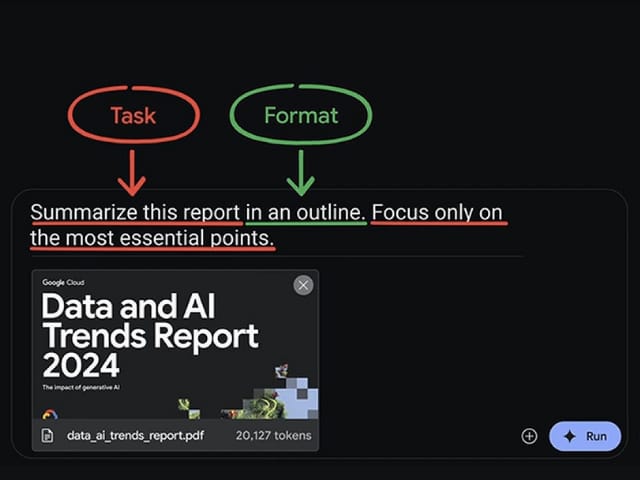
You can also include a Persona to specify the summary for specific audiences. For example, if someone struggles with numbers, you could prompt:
“Summarize this for someone who isn’t good with numbers.”
Use chain of density prompting to summarize texts
However, AI summaries can sometimes be too broad. To refine the output further, the course introduces a method called Chain of Density Prompting. This technique helps you produce increasingly concise summaries by iterating your prompt step-by-step.
To do this, let’s use our last prompt as the example:
Task:
“Provide a shorter summary focusing on the report’s top 2 to 3 trends.”
Want it even shorter while highlighting the most important part?
Task:
“Condense the summary into a single sentence.”
Format:
“Into a single sentence”
Context:
“Highlighting the most dominant trend.”
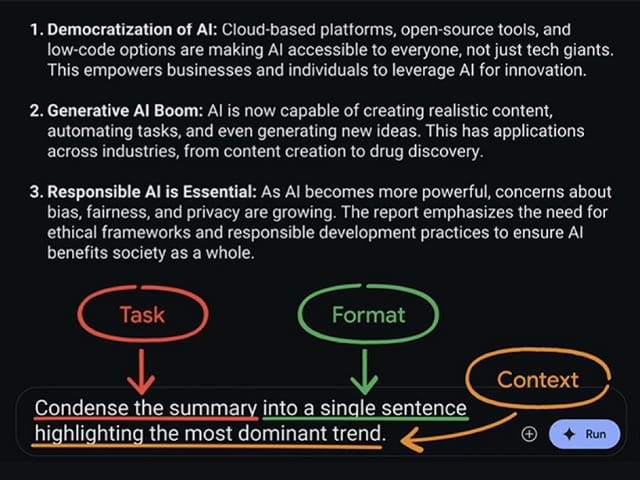
You might wonder why we do not just ask for a short summary right away. The reason is that iterating helps reduce the risk of hallucinations by moving from a detailed summary to something more to the point.
Chain of Density Prompting can also be applied in reverse. If the response is too short, you can prompt the AI to output a longer response and include more details.
Module 3: Speed Up Data Analysis and Presentation Building
Videos: 8 | Readings: 3 | Assignments: 2
Module 3 builds on the concepts from Module 2 by introducing more real-world use cases, this time focusing on data analysis and presentation building. A reminder from this module is the importance of data privacy. The course advises against entering sensitive or confidential information into AI tools, especially when working within a company.
Analyze Data with AI
If you’re not good with using Google Sheets or Excel, this part of the course shows you how to analyze data using AI. In this lesson, the course uses a sample dataset from Kaggle (a data science company).
The dataset includes information from a grocery store chain:
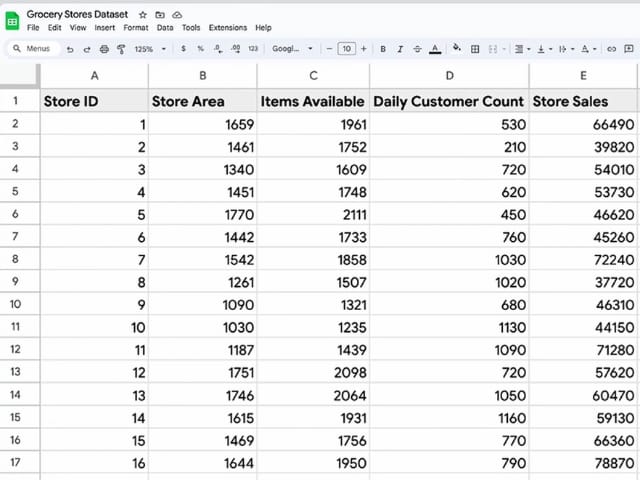
The image above shows a dataset with information about a grocery chain.
The goal is to analyze the data to identify trends and patterns that can help improve how the company operates. But before diving into insights, we need to organize the data to make it easier to work with.
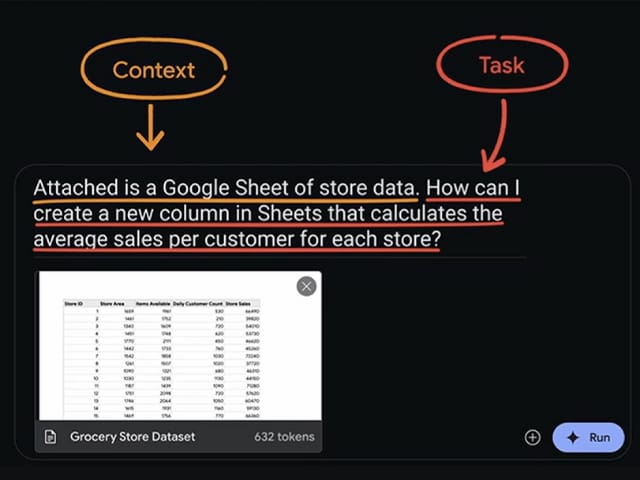
Context:
“Attached is a Google sheet of store data.”
Text:
“How can I create a new column in sheets that calculates the average sales per customer for each store?”
If the initial method of organizing the data doesn’t give the expected result, you can always iterate your prompt to refine the output. Next, you can dive deeper to uncover trends in the data.
Text:
“Give me insights into the relationship between “Daily Customer Count,” “Items Available,” and “Sales” based on the given data.”
Based on this prompt, Gemini was able to identify useful patterns, such as the lack of correlation between the number of items in a store and its total sales.

With the help of gen AI and a few prompts, you no longer need to spend hours analyzing data. Instead, let AI do the heavy lifting and deliver useful insights in less time.
Build Presentation with AI
Generative AI can help you turn your ideas into compelling presentations by organizing your content into a clear narrative, generating talking points, and even creating visuals to keep your audience engaged. In the final chapter of Module 3, the course walks through how to create a prompt to build a presentation for a headphone company.
First, let’s prompt Gemini to help outline the structure of the presentation and summarize the findings.
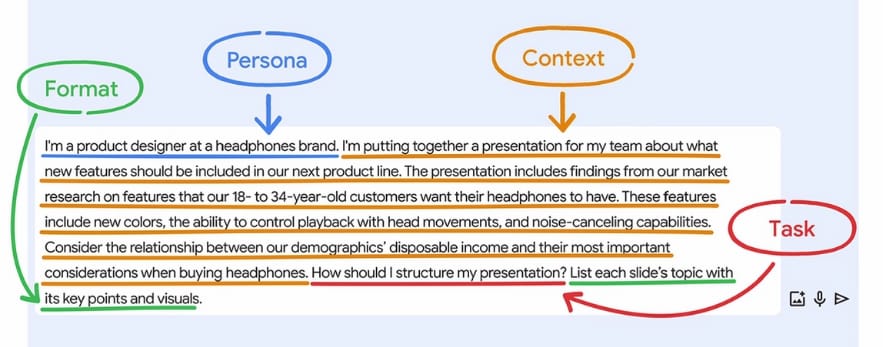
Persona:
“I am a product designer at a headphones brand.”
Context:
“I’m preparing a presentation on proposed features for our next headphone line, based on market research targeting 18- to 34-year-olds. Key features include new colors, head-motion playback controls, and noise cancellation. Consider how disposable income influences their purchasing priorities.”
Task:
“How should I structure my presentation?”
Format:
“List each slide’s topic with its key points and visuals.”
The AI-generated response provides a complete slide-by-slide structure, including a title slide, a contextual introduction, detailed key point breakdowns, and a call to action at the end.
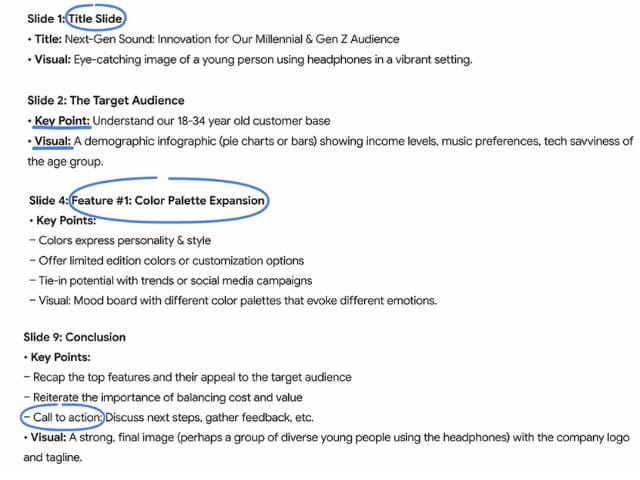
In the next part of the lesson, you will learn how to prompt AI to generate images that complement your presentation.
Create Image with AI
After building the presentation in the previous lesson, the next step is to add visuals that make the presentation more engaging and informative. When using gen AI for image generation, you want to use the prompting framework along with a few additional elements to generate the perfect image prompt.
When crafting image generation prompts, be sure to include the following:
- Size
- Color
- Position
- Aesthetic
First, we’ll define the task and format. Let’s start with the task:
Task:
“Generate close-up images”
Context:
“of a pair of sleek, silver headphones on a desk in a college dorm room. They should have musical notes floating around the headphones to show that they’re playing music.”
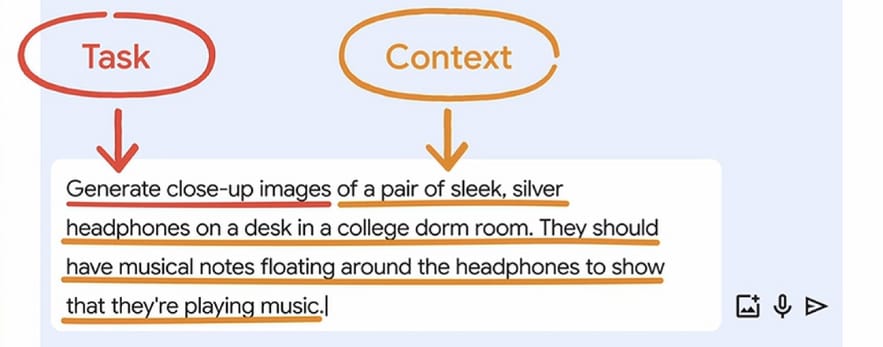
After generating your images, always evaluate the output just like you would with AI-generated text. Make sure the visuals align with your vision in mind and are free from errors. Also, remember to include a disclaimer whenever you use AI-generated images in your work.
Module 4: Use AI as a Creative or Expert Partner
Videos: 13 | Readings: 6 | Assignments: 4
We’ve reached the final module of the course, and it’s an important one. This module dives into more advanced and creative ways to use AI. It covers techniques such as prompt chaining, the different types of prompt chaining, how to create your own AI agent, and how to build your own prompt library to improve your workflow.
Prompt Chaining
Sometimes, when working on more complex tasks, it helps to take the output from a gen AI tool and use it as context for a new prompt. This technique is known as prompt chaining.
Let’s say you’ve just finished writing a fantasy novel inspired by Harry Potter, from the example in Module 1. Now, you need to promote your novel, so you decide to create a marketing plan.
First, let’s use the prompting framework to generate a tagline:
Task:
“Generate three options for a one-sentence summary of this novel manuscript.”
Format:
“The summary should be similar in voice and tone to the manuscript but more catchy and engaging.”

Next, let’s refine the tagline to focus on a specific theme in the story:
Task:
“Create a tagline that is a combination of the previous three options.”
Context:
“With a special focus on the exciting plot twists and mystery of the book.”
Format:
“Find the catchiest and most impactful combination. The tagline should be concise and leave the reader hooked and wanting to read more.”
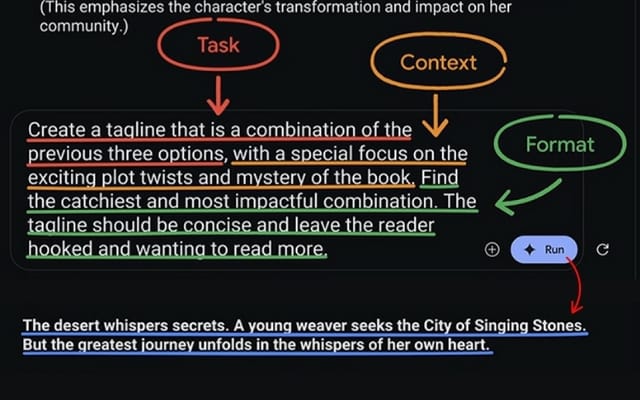
Now, let’s write a blurb for the back cover of your novel:
Task:
“Create a five-sentence summary of the entire manuscript below that expands on the one-sentence summary.”
Format:
“five-sentence”

After generating your blurb, let’s move on to planning where you’ll promote your novel:
Task:
“Generate a six week promotional plan for a book tour, including what locations I should visit and what channels I should utilize to promote each stop on the tour.”
And just like that, with a series of connected prompts, AI helps generate a tagline, a blurb, and a promotional tour plan for the novel.
It’s important to note that prompt chaining is not just about adding more context to your prompts. It’s about expanding on previous outputs to guide the AI for further incoming prompts.
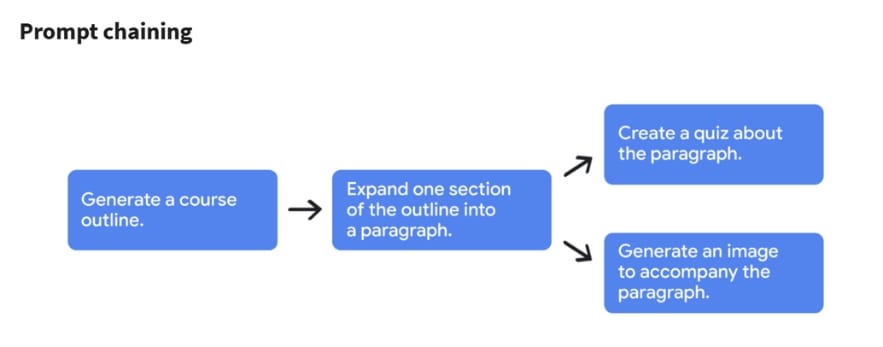
One important consideration when using prompt chaining for your work is that you’ll need an AI model with a long context window. This enables the AI to process and retain more information throughout the conversation for more accurate results.
2 Types of Advanced Prompt Chaining
After exploring the concept of prompt chaining, let’s take it further by diving into the two advanced types of prompt chaining techniques.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
When using gen AI like ChatGPT or Gemini, sometimes you don’t just want an answer. You want to understand how the AI came up with that answer. This is where Chain of Thought Prompting comes in.
In simple terms, Chain of Thought Prompting is a technique where you ask the AI to explain its thinking process step by step. Instead of giving you the final answer right away, it shows its reasoning, just like when your math teacher asks you to show your work.
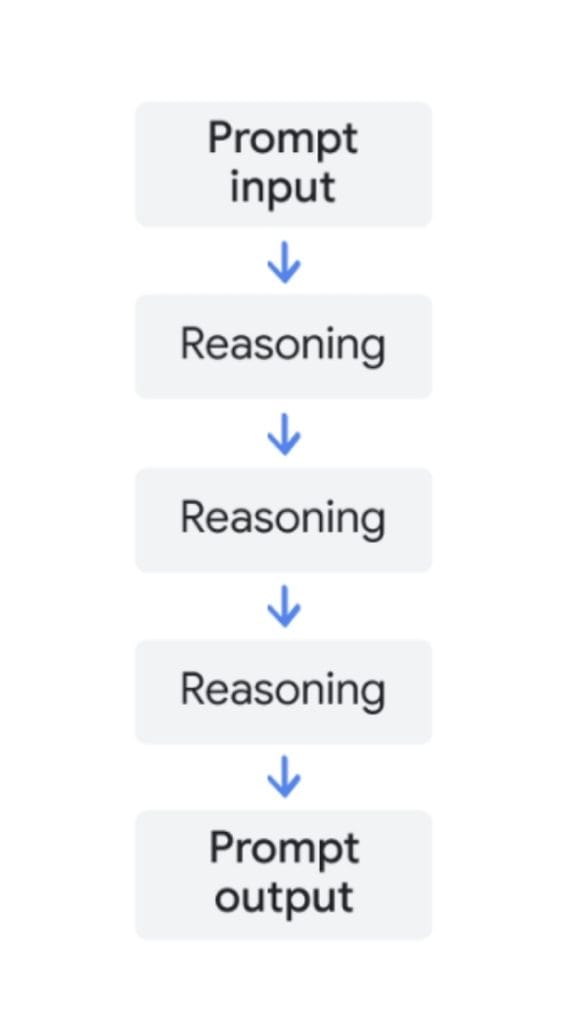
You can trigger this by using key phrases like “explain your reasoning” or “go step by step” to instruct the AI to break down its reasoning.
Tree-of-Thoughts Prompting
Tree of Thought Prompting is a technique that explores multiple solutions to a single prompt. Instead of following a single chain of thought, the AI gives you several responses to compare and let you pick the one you like.
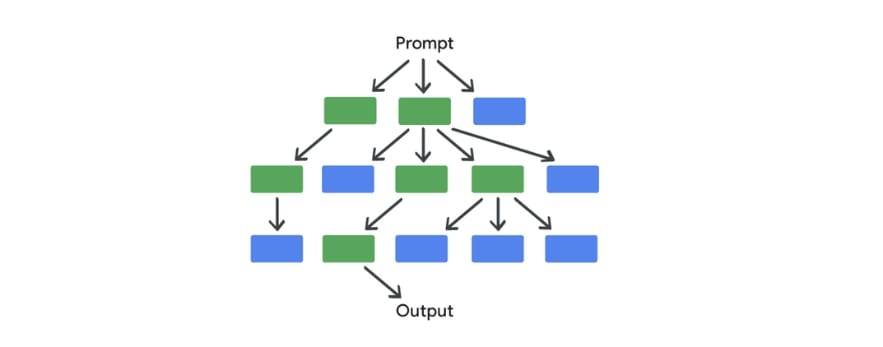
For example you’re generating an image for your novel. With tree-of-thought prompting, you might use a prompt like this:
Imagine three different designers are pitching their design to me.
All designers will write down one step of their thinking, then share it with the group. Then all experts will go on to the next step, etc. If any expert realizes they’re wrong at any point, then they leave.
The question is: Generate an image that’s visually energetic, and features images of art supplies and computers. Show me three suggestions in very different styles from simple to detailed and complex.

“I like the second one. Now generate three other variations of that style.“
So now you get the point, you can keep repeating this process and explore different branches of the tree until you end up with something you like.
AI Agent
An AI Agent is a gen AI tool that acts like your personal expert or assistant. It can assist you to solve problems or learn new things. There are various types of AI agents, such as business agents that help grow your company, coding agents that debug your code, and even AI companions that can be buddies with you.
In this module, you’ll explore two types of AI agents:
Agent Sim
The first type is Agent Sim, which simulates real-life scenarios like job interviews or difficult conversations. It allows you to practice responses and adjust your approach as needed.
Let’s design an Agent Sim to simulate a training program for interns to improve their interview skills.
Persona:
“Act as a career development training simulator.”
Task:
“Your task is to help interns master interview skills and conduct conversations with potential managers.”
Context:
“You need to support the following types of conversations:
- Articulating strengths and skills
- Communicating professionally and confidently
- Discussing future career development goals
Once an intern has picked a conversation topic, provide details about the situation and the interviewer’s role. Then act as the interviewer and allow the intern to participate as the employee. Make sure to guide the conversation in a way that will allow the intern to exercise their interview skills.”
After this, you want to include a “Stop Rule” in your prompt to let the AI agent know that the simulation is complete and to provide feedback on how you could have improved the interview.
Stop Rule:
“Continue the role play until the intern replies with “JAZZ HANDS.” After the intern gives the stop rule “JAZZ HANDS,” provide them with key takeaways from the simulation and skills they can work on”

Agent X
The second type is Agent X, which provides expert-level feedback on any topic you specify. Think of Agent X as your personalized consultant.
Let’s create an Agent X to review and critique a pitch presentation for a potential client.
Persona:
“You’re my potential client, the VP of Advertising at a world-famous sports car company known for its innovation, performance, and engineering excellence.”
Context:
“You’re considering hiring a creative agency to develop a new campaign that will attract a younger generation of buyers. You are in a meeting with me, the design director of a creative agency that’s pitching a new campaign for your company.”
Task:
“Act as my potential client. When I provide answers, critique the answers. If needed, ask follow-up questions.”
Stop Rule:
“Continue the conversation until I give the stop rule “BREAK.” Then give me a summary of the whole conversation highlighting ways I can improve my pitch.”
References:
“I’ve included the brief the car company provided me that has all the relevant information for this project. Use the information from this brief to inform your answers.”

Create Your Own AI agents
To create an AI agent, you’ll need to use the prompting framework, focusing primarily on the persona and context.
Here’s how to create your own an AI agent:
- Assign a persona
Decide on the role you want the generative AI tool to take on.
Example: “Act like a successful personal fitness trainer and talented nutritionist.” - Provide context and scenario details
Describe the situation or background information that will guide the AI’s responses.
Example: “I’m looking to improve my overall fitness and adopt a healthier lifestyle.” - Define the conversation type
Explain what kind of interaction or support you expect from the AI.
Example: “Ask me about my workout routines and meal planning, and give me feedback.” - Include a stop rule
Add a phrase that tells the AI when to end the conversation.
Example: “When I want the conversation to end, I’ll write, ‘no pain, no gain.’” - Ask for a summary and advice
Instruct the AI to give you a recap and tips once the session is complete.
Example: “At the end of our conversation, provide a summary of the advice you provided.”
Pro Tip: The more specific and detailed you are about the role, context, and behavior you expect, the more helpful and accurate your AI agent will be.
Conclusion and Writer’s Note
And that is it, you have completed Google Prompting Essential Course, whether you should take the course, it’s up to you, but if you don’t mind spending $49 on the course to elevate your portfolio then you should take it.
But if you’re just purely here for the lessons and knowledge without wanting to spend a single dime, then I recommend you to learn from this curated post here and save hours of your time. I’ll also be attaching a playlist of all the videos from the Google Prompting Essential Course (Free on Youtube) for those who want to view the full videos of all 4 modules in the course (without the readings, assignments and certificate).
Click here to view the playlist.
I hope you guys enjoy our journey together from writing simple text prompts to creating our own personal AI agents. All of these are possible thanks to Google for making such a detailed AI prompting course, Coursera for providing an intuitive platform to host the course, Tina Huang for inspiring me to make this post and especially to all of you for taking your time to read this article and learn together.
This is Moses Giroth signing off—happy learning!